
What is a contract for difference (CFD)?
Essentially, a CFD is a type of financial derivative that allows you to speculate on a variety of financial markets, such as stocks, indices, commodities, and forex pairs. With CFDs, you don’t actually purchase the underlying assets themselves, but rather, you trade on the predicted rise or fall in their price over a short period of time.
To put it simply, a CFD is a contract between a trader and a broker, in which they agree to exchange the difference in value of an underlying security between the beginning and the end of the contract, typically within a day. This type of trading is popular among investors who are looking to make quick profits by taking advantage of small price movements in the market. If you’re interested in CFD trading, this guide will provide you with everything you need to know to get started.
A contract for difference (CFD) is:
- A derivative – you do not own the underlying asset
- An agreement between you and your broker
- Based on the change in an asset’s price
- Conducted over a short time period
CFDs Explained: Understanding Contracts for Difference Trading
A contract for difference (CFD) is a trading instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various underlying assets without actually owning the asset itself. Here’s how it works:
What are CFDs?
A contract for difference (CFD) allows you to trade using a fraction of the value of your trade through trading on margin, or leveraged trading. This enables traders to open larger positions than their initial capital may allow, giving greater exposure to global financial markets.
Buying and Selling with CFDs
One of the benefits of CFD trading is the ability to speculate on the asset’s price movements in either direction. You can buy or sell a contract, opening a long or short trade, depending on your belief of the asset’s price movement.
Keep in mind that leverage trading can increase your profits, but also amplify your losses.
How does CFD trading work?
When you open a CFD position, you choose the trade size you want to buy or sell. Your profit will rise or fall with each point the market moves in your favor or against you. However, there is a risk of loss if the market moves against you.
If you believe the asset’s price will rise, you would buy a long position, and if you believe the price will fall, you would sell a short position. Either way, you risk making a loss if you are incorrect.
What is a CFD account?
A CFD account allows you to trade on the price difference of various underlying assets using leverage. With a deposit margin, you only need to put up a fraction of the amount needed to trade.
The maintenance margin needs to be covered by equity, which includes the account balance with unrealized profits and losses. Your account’s equity must always cover the maintenance margin to keep your positions open, especially in case of running losses, or you risk receiving a margin call.
Before offering margin trading, your broker may need to know a little about you, so they’ll ask you to set up an account and provide proof of identity and your ability to cover losses. Many brokers offer a demo account for practice before trading live.
Some regulators require new customers to pass an “appropriateness or suitability” test, meaning answering questions that demonstrate their understanding of the risks of trading on margin. It’s best to educate yourself on how leverage and margin work before trading.
Some experienced traders may set up multiple CFD accounts with the same broker to trade different assets or follow alternative trading strategies.
Understanding Leverage in CFD
Trading In CFD trading, leverage is a common term that refers to holding a position that requires a fraction of the full trade value. When you trade CFDs, you borrow funds from your broker to make up the difference between the full value of the trade and the amount you put down. It is essential to note that leverage can amplify both your profits and losses.
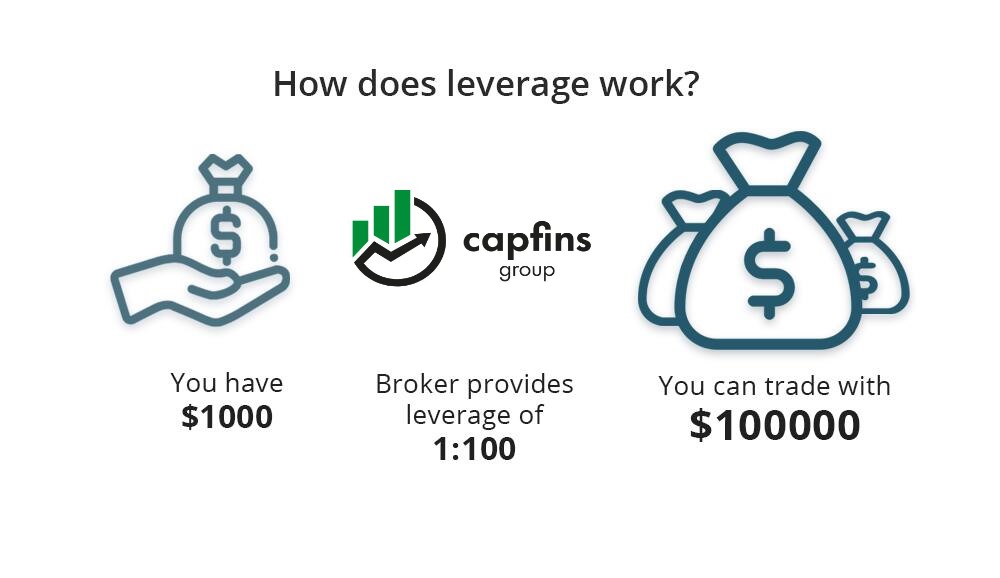
Trading on Margin
Leveraged trading is commonly known as trading on margin. The percentage of the value you must deposit can differ, but it is usually a small portion. For example, if your CFD provider requires a 10% margin, you would only need to deposit 10% of the trade’s total value.
Margin Example
For instance, suppose you want to buy $1,000 worth of Brent crude oil, and your broker asks for a 10% margin. In that case, you only need to deposit $100 as the initial amount to open the trade. The remaining $900 will be covered by your broker.
Understanding CFD Trading: Spread and Commission Explained
When it comes to trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs), there are two prices you need to be aware of: the buy price (also known as the ask price) and the sell price (also known as the bid price). These prices are based on the value of the underlying instrument and are always set higher and lower than its current value, respectively. The difference between the two is referred to as the CFD spread.
At Capfins.com, we offer commission-free CFD trading, which means that you won’t be charged for opening or closing trades. When you open a long position, you start at the buy price, and when you close your position, you sell at the current bid price. Conversely, when you open a short position, you start at the sell price, and when you close your position, you buy at the current ask price. By understanding how these prices work, you can make informed trading decisions and manage your risk more effectively.

What is the contract length of CFDs?
CFD trades on Capfins.com typically have no fixed expiry date, meaning the CFD contract length is unlimited. The trade is only closed when placed in the opposite direction. For example, a buy trade on 100 CFDs can be closed by selling the CFDs.
However, if you wish to keep a daily CFD trade open after the cut-off time (usually 10pm UK time, but it may vary for international markets), you will be charged an overnight funding fee. In forex, index, and commodities trading, Capfins.com charges an overnight fee on the full trade size, while for stocks and cryptocurrencies, the charge is only applied to the borrowed portion.
Advanced strategies for risk management using CFDs
CFDs are complex instruments with high risks. Therefore, it is crucial to implement an appropriate CFD risk management strategy. Once you have set up your account and devised a trading plan, it is important to determine the amount you are willing to risk.
If you are risk-averse, consider opportunities with lower risk-to-reward (R-R) ratios. For slow and steady growth, asset classes with higher volatility should constitute only a small part of your portfolio. Diversification across all asset classes can increase the likelihood of attractive trading opportunities and mitigate risk.
Stops-loss and take-profit
Consider setting up limit orders to automatically close a position at a given profit level so you do not have to monitor the market constantly. Take-profit orders reduce the likelihood of holding on to a profitable trade for too long and seeing the price fall again.
You can also place stop-losses to mitigate CFD risks and restrict potential losses. A stop-loss is triggered at the level indicated earlier by the trader and executed at the next available price quotes. Note that in volatile markets, lack of liquidity or large order sizes may result in slippage. Guaranteed stop loss can protect against slippage, yet it comes at a fee.
Negative balance protection and margin closeout
CFD brokers are required by regulators to provide negative balance protection. Capfins.com provides negative balance protection for CFD accounts. To keep positions open, a trader must meet the maintenance margin requirement, which must be covered by the account’s overall equity.
If the account equity falls below the maintenance margin, Capfins.com will notify the trader via a ‘margin call’. The trader must either top up their balance or close some positions to reduce exposure.
If no action is taken and the close-out level is reached, Capfins.com will gradually close out the trader’s positions. With negative balance protection, a trader’s account balance is corrected if it drops below zero. If the market suddenly moves against a trader, Capfins.com can close the affected position to protect them.
Hedging
Hedging is a crucial risk management strategy used by experienced traders to reduce losses. CFD hedging provides an opportunity to protect an existing portfolio by speculating on a price downtrend through selling short.
Hedging is a risk management approach employed to minimize losses. The purpose of hedging is to safeguard your profits or capital, particularly in times of uncertainty. The basic concept is that if one investment incurs a loss, your hedge position generates a gain.
Advantages of Hedging
Following are the various advantages of Hedging:
- Futures and options are very good short-term risk-minimizing strategy for long-term traders and investors.
- Hedging tools can also be used for locking the profit.
- Hedging enables traders to survive hard market periods.
- Successful hedging gives the trader protection against commodity price changes, inflation, currency exchange rate changes, interest rate changes, etc.
- Hedging can also save time as the long-term trader is not required to monitor/adjust his portfolio with daily market volatility.
- Hedging using options provide the trader an opportunity to practice complex options trading strategies to maximize his return.
Disadvantages of Hedging
Following are the disadvantages of Hedging:
- Hedging involves cost that can eat up the profit.
- Risk and reward are often proportional to one other; thus reducing risk means reducing profits.
- For most short-term traders, e.g.: for a day trader, hedging is a difficult strategy to follow.
- If the market is performing well or moving sidewise, then hedging offer little benefits.
- Trading of options or futures often demand higher account requirements like more capital or balance.
- Hedging is a precise trading strategy and successful hedging requires good trading skills and experience.

